Online Privacy in eCommerce: 6 Key Takeaways and Shocking Stats You Didn’t Know About

This blog post was originally contributed by Jason Chow, a Marketing and Outreach Manager at WebHostingSecretRevealed.net (WHSR).
The eCommerce landscape has changed much since the early days of Amazon.com. Technological innovation fueling this industry has allowed the explosive growth of cross-border trade. It is expected that by 2021, retail eCommerce sales will reach almost $4.9 trillion.
Yet this massive industry has grown beyond the major eCommerce companies, and new competitors are entering the market. Developing technologies such as in digital payments system processing and shipping models have enabled even the smallest companies to join the eCommerce scene.
In such a lucrative market, data has become the new oil. Both cybercriminals and regulators are increasingly looking towards eCommerce sites from different sides of the field.
As eCommerce merchants, are you aware of what is going on regarding user data in real life? How do you protect your privacy online? And, what you should know about eCommerce website privacy?
1. Three Billion Data Records Were Compromised in 1H 2018

According to the Gelmato Breach Index, there have been more than 14 billion data records lost or stolen since 2013. Of those, more than 3 billion in the first half of 2018 alone. Two of the main causes were cybercriminals and accidental loss.
The age of digital has expanded the use of technology around the globe. eCommerce platforms are one of the major congregation points where large amounts of user personal data are stored. With data breaches on the upward trend, how prepared are you in safeguarding the privacy of your customer information?
Suffering from a data breach can have a very significant impact on any digital platform or social media sites. As an example, Google closed it’s Google+ platform (the social networking site) after the exposure of more than half a million Google+ users’ data. Where eCommerce is concerned and payments information is involved, the impact on internet privacy protection will be even greater.
- Data records compromised in H1 2018 showed a 72% increase over the previous year
- 59% of all data breaches affected United States residents
- More than 700,000 records were lost each hour in 2018
(All statistics above were drawn from Gelmato)
Because not all data is stolen from external sources, it would be a good idea to ensure a digital audit and log system is implemented. These elements play a significant role in eCommerce security. Through the logs and audit program would be able to track all network activities. This will include file manipulation activities such as copying, downloads, or deletions as well as have contact information.
Additional Resources:
- Microsoft Guide to File Server Access Audit
- IBM Introduction to file audit logging
- Learning about permanent audit files
2. Web Hosting Plays a Part in Your Security
As online businesses, your website hosts plays a part in many facets of your security, and that includes helping you safeguard the privacy of your user data. On one part, they are the physical access point to your user data, while on another, they are responsible for monitoring their equipment and infrastructure that runs your website.
There is simply no avoiding it, and this is something that applies universally, from the cheapest web hosting to the ultimate solutions. Cheap doesn’t always mean bad and much depends on how your web host directs its business.
To get an idea of how well your web hosting provider is meeting your security needs, consider if they offer: backup and restore options, secure server capabilities, malware scanning, or any other security-related features.
If you’re concerned about the cost of web hosting, consider these facts as well:
- Private data security breaches cost an average of $3.86 million.
- Online businesses losing less than 1% of customers due to a data breach suffered average losses of $2.8 million.
- Yahoo paid $85 million to settle a massive corporate data breach between 2013 to 2014.
As you can see, the potential financial loss can be significant where data loss is concerned. That’s not even taking into consideration the damage it might cause to your brand as well. Take the time to choose the right web hosting provider when building an eCommerce website, and you’ll have your security needs met halfway.
Additional Resources:
- Most popular website host in terms of usage
- Sucuri is an excellent third-party web security provider
- WordPress has many great security plugins
3. Understanding and Complying with GDPR
GDPR is a regulation introduced as an update to the EU Data Protection Directive. It was designed to suit all EU member nations and help citizens in those countries maintain their right to data privacy.
For those who may be thinking that GDPR is European Union centric, it should come to mind that eCommerce truly is borderless in most cases. Unless you are planning to serve only selected markets, most major global regulations need to be considered.
Any company that finds itself processing data of any EU citizen will be subject to the confines of the GDPR. Smaller companies might think that they can get away with disregarding this regulation since most will not have an EU presence.
Unfortunately, the GDPR dictates that an EU representative must be established for any company falling under the GDPR purview. This means that if you are or intend to process data of EU citizens (payments or otherwise), you need to appoint an EU representative.
- More than 33,000 complaints on GDPR violations have been filed in the UK.
- EU data protection authorities have started 255 cross-border investigations.
- Fewer than 100 fines were imposed under the GDPR between May 2018 to January 2019.
The first step towards complying with the GDPR is to understand the key concepts of it since it needs to be applied organization-wide. This needs to be followed by a data mapping exercise and the establishment of a privacy policy.
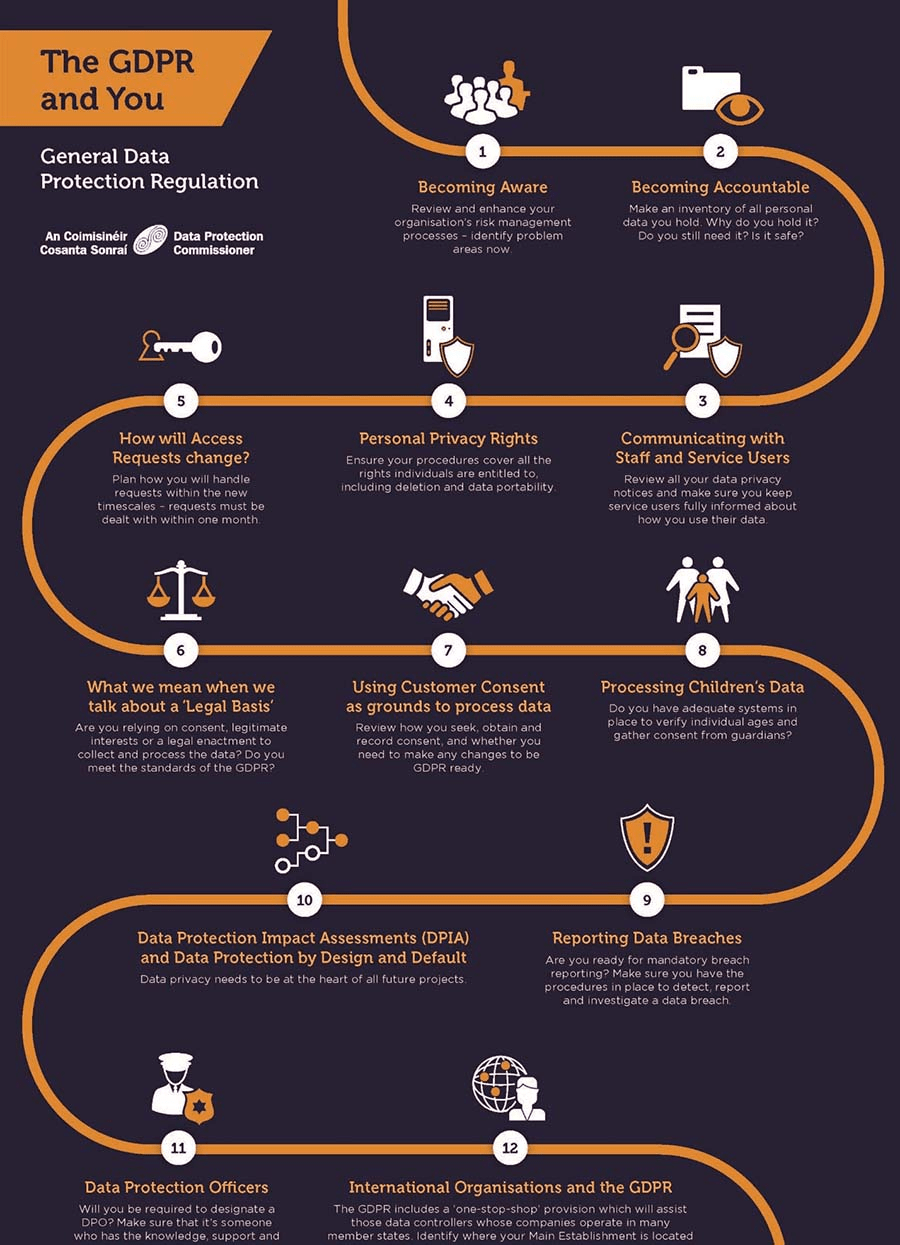
Caption: Data Protection & you (Source: Data Protection Commission)
Some of the areas you need to take data security standards into consideration include:
- Data protection impact assessment
- Disclosure
- Assignation of data protection officers
- Data processing of minors
- Auditing
Additional Resources:
- GDPR home page
- Companies abusing data privacy regulations
- Understanding the age of consent under GDPR
- Data Map Template for GDPR
- European Supervisory Data Protection Authority
4. Using SSL for Better Protection
Although much web privacy places focus on the data that is stored by websites, information such as credit card details, can also be stolen during transmission. This means that while a user is in the process of providing you with personal information, it can be intercepted.
Major search engines such as Google along with Internet browser developers recognize this and have placed increased emphasis on the transmission of data to and from users to websites. For example, Google penalizes websites on their search rankings which don’t implement Secure Socket Layer (SSL) certification.
SSL is a method which helps you encrypt all information passed between individual web browsers and your website. This helps keep it secure and private so users can provide information with peace of mind. If you haven’t already implemented SSL certification, it is time to seriously consider it.
- Basic signed SSL certificates can cost as little as $15 annually.
- Paid SSL certificates usually come with varying warranties against loss.
- 93% of all sites listed on Google are already SSL-compliant
There are various types of SSL with varying degrees of security assurance for consumers. There is even a free SSL certificate provided by Let’s Encrypt. If you are HTTPS compliant (meaning you have any SSL installed), your search rankings will not be affected.
Additional Resources:
- Thawte and Comodo are two of the more recognized SSL providers.
- Installing SSL in WHM
- Six SSL options for your business
5. California has a Specific Privacy Act
The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) was introduced in mid-2018 and will be fully active at the beginning of 2020. It is intended to empower residents of the state regarding their personal data. With this act, they were given the right to know what information was being collected about them and whether it is sold or otherwise disclosed.
More significantly, it also allowed them to deny rights to any site that wished to sell their data. Finally, under the CCPA, they were also guaranteed equal prices and services even if they exercised their rights to privacy under the act.
It is important to note that this act specifically targets certain ‘brackets’ of companies. To fall under its purview if you’re doing business with California residents, your company must either:
- Gross more than $25 million annually
- Trade in the personal information of residents at a volume of over 50,000 annually or;
- Earn more than half your annual revenue from such activities
From the above, you can see that many businesses will likely fall through the cracks and not necessarily have to be concerned about compliance. However, the act is still being revised, and future amendments may increase restrictions before it comes into force.
To best plan for CCPA, it would be wise to consider amendments to existing privacy policies. The best way to do this would be to:
- Create a California-specific clause or a new form for the State.
- Ensure that California consumer rights are clearly stated and described
- List all facets of information potentially collected by your business.
- Most importantly, if you do not sell user data, ensure that you explicitly state so.
Additional Resources:
- CCPA Home Page
- Other states with similar laws include (but are not limited to) Arizona, New York and New Jersey.
- Breach of the CCPA can result in fines of between $2,500 and $7,500 per violation.
- The law is expected to affect half a million companies in the United States
- PwC CCPA readiness roadmap
6. You Can Generate a Privacy Policy for Free
Knowing the impact of data privacy on business is one thing, but safeguarding against it is another. For smaller businesses who try and achieve compliance, the task of navigating numerous regulations that possibly span the entire globe can be a huge challenge.
Across the world, 80 countries are known to have data privacy laws, and that isn’t even counting more streamlined laws for individual states. As we mentioned in the section above, the United States alone has many states with their own privacy laws or acts.
Failing to comply with data privacy regulations can result in significant fines. Thankfully there are options for this designed for small businesses. You can use online tools to generate privacy policies that help you comply with data privacy laws.
Sites like FreePrivacyPolicy and PrivacyPolicyGenerator offer basic privacy policy automation services. Of course, there is a catch to it. Most of these free generators offer template services which may not be an idea for your business practices.
They often charge extra fees for sites that are meant for commercial purposes, such as Online Stores. The policies they generate are also often only compliant in a general sense, with specific provisions for major laws such as GDPR.
For smaller eCommerce businesses, one way of using them would be to generate the framework with the tool and consult with legal counsel to fine-tune it to your needs. This might help lower the overall legal fees involved.
Additional Resources:
- Termly Privacy policies for the EU
- Privacy and cookie policy guide for website owners
- Understanding a privacy policy with WikiHow
Conclusion: It Isn’t as Difficult as it Looks
By now, there might be a slight concern on your part regarding security and data privacy. However, I would like to bring the focus back down towards two key takeaways from the points contained above.
The first is that web security isn’t a single thing but has many facets which need to be addressed one at a time. The good thing about this is that you can create a checklist and look towards them incrementally as improvements over time.
The second is that there are varying degrees of security that fit different levels of businesses. Data security and privacy aren’t applicable to major eCommerce sites alone, but there are more scaled-down options available for smaller businesses.
These two takeaways should help put your mind more at ease, and if you make concrete plans to move forward on the security aspect of your business, you should be fine over time. Remember, it is really a matter of balance, and no two businesses are identical.Through awareness of the issues involved, you can come up with a long term custom plan of progress that is specific to your needs. Much as building the perfect business is impossible, so too is perfect eCommerce security, but we can always try.

Alex joined X-Cart in 2005 and since then spearheaded Support and Hosting departments, focused on customer needs as a Director of Customer Success and now helps our clients to grow and prosper as Enterprise Account Executive. He truly believes that if we don’t take care of our customers, someone else will.